5 TOP TIPS FOR HEALTH
5 TOP TIPS FOR HEALTH
Tip 1. Eat 'real food'
The definition of food is ‘any nutritious substance eaten to maintain life and growth’. The problem is that many of the items in our pantry have been grown in substandard soils, are sprayed with herbicides, pesticides, dried, heated, frozen or processed with preservatives, flavourings, high sugar, trans fats and colourings. In short most consumables are not nutritious at all and many are in fact detrimental to health.
So my first step to a healthy life is ‘eat real food’ – that which is as close to nature as possible. The three main food groups required for human health include protein, fat and carbohydrates. In these foods are found everything necessary to keep the human body functioning optimally.
Remember the reason we eat is to stay alive. Eat foods that will keep you healthy longer.
|
Proteins (amino acids) are the building blocks of life growing and maintaining our structure including our ligaments, muscle, organs and skin. There are 9 essential amino acids (complete proteins) mostly from animal sources. The other 11 amino acids are non essential as they are made in the body and also gained by eating nuts, fruit, vegetables, legumes and grains. |
Carbohydrates provide fuel for energy to keep us moving and even thinking. There are three types of carbs – sugar, starch and fibre. The best type to eat are unrefined simple (fruit, vegetables, dairy) and complex (starchy veges and fibre) while sugars should be limited to vegetables and fruits. |
Fats (saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats and essential fatty acids) are essential and the best sources are natural and unprocessed. They grow and maintain our cell membranes and organs. Avoid highly processed trans fats which are associated with many diseases, as they can damage the cell membrane permeability. |
Tip 2. SLEEP - better than medicine.
Our body heals on many levels while we sleep.
Rest activates the parasympathetic nervous system enabling the body to digest nutrients and maintain and repair our memory and brain function, energy levels, mood, the immune system and our ability to cope with stress. Night and day affect the body in different ways, called the circadian rhythm (a 24 hour cycle) where a number of hormones have different roles.
- As daylight diminishes the pineal gland in the brain secretes melatonin which induces sleep.
- Early in the night growth hormone is secreted which helps the body to grow and heal.
- Serotonin is releasedand consolidates memories and nurtures the brain.
- Cortisol is available close to the time of waking, elevating our blood glucose levels in time for new activity and adding a ‘bounce’ to our step.
- The morning light seeping in through our retina then signals melatonin to dissipate for the day.
If we ignore our natural rhythm and go to bed too late, these hormones are upset, and under perform. This can affect our ability to handle our emotions and to think straight. It can contribute to high blood pressure, weight gain, diabetes, heart disease and a number of anxiety illnesses.
How much sleep do we need?
Each individual’s sleep requirements are different and people seem to need less sleep as they age – but a good night’s sleep, whoever you are, should leave you waking up refreshed. It is better to go earlier to bed than to sleep in. Non Rem (rapid eye movement) sleep happens between 11pm and 3am and this is when our body regenerates and repairs.
Dreaming:
Dreaming occurs at intervals throughout the night during REM (rapid eye movement sleep) and may give the brain a chance to work through the days events in dream imagery, perhaps even eliminating an overburden of thought from that day– in a way clearing the neuron network.
Dreaming is hindered by the absence of vitamin B6 in the body.
Sleep can be enhanced by:
- Reducing your daily stress – this increases Cortisol production in the evening giving you a second wind and thereby reducing the morning Cortisol which gives you that get up and go
- Write down your jobs for the following day so they do not weigh on your mind
- Go to bed in a darkened room (as light disrupts the circadian rhythm).
- Don’t go to bed hungry
- Reduce coffee intake
- Take Magnesium to help the body relax, Tart Cherry juice which contains melatonin, Chamomile tea or herbs such as Passion Flower and Kava.
- Deep breath or do some gentle exercises prior to going to bed to put you into a parasympathetic state
COPD
Pulmonary Disorders
Lung disease is influenced by conditions of the environment, occupation and personal and social habits such as smoking.
It has three clear classifications:-
- Acute or chronic,
- Obstructive or restrictive and
- Infectious or non infectious.
OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASES
These are characterised by airway obstruction that is worse with the out breath, (where more muscle is needed, and emptying of the lungs can be slowed).
The most common obstructive lung disease is asthma as well as chronic bronchitis and emphysema also prevalent. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Asthma too can be chronic but it is typically more acute and intermittent.
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)
Unlike asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD represents pathological lung changes as seen in emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It is both preventable and treatable.
Airway obstruction can be due to loss of supporting elastic recoil, from the lung tissue, and/or tube narrowing as a result of airway wall thickening.
Risks include:
- GeneticsSmoking
- Exposure to air pollution
Symptoms include:
- Breathlessness
- CoughPhlegm production
- Recurrent respiratory infection
- Wheezing
Complications:
- Bacterial and viral infection
Herbal medicine and nutrition will
- Remove mucus
- Relieve symptoms
- Improve immunity
- Reduce inflammation
INCLUDE:
- Fresh seasonal fruit and vegetables should make up the largest percentage of the diet
EXCLUDE:
- GrainsCarbohydrates – biscuits, jams, cakes‘Saturated’ fatsMucus producing foods – dairy (milk, cheese, ice cream), wheat
CHRONIC BRONCHITIS
This is defined specifically as hypersecretion of mucus with a chronic chough producing phlegm usually caused by cigarette smoking or air pollution.
Chronic Bronchitis on right
Inspired irritants result in airway inflammation which causes bronchial swelling and increased mucous production that cannot be cleared because of impaired ciliary function. Infections can exacerbate the condition. As the airways become increasingly narrowed, expiratory airway obstruction results. Extensive air trapping puts the respiratory muscles at a mechanical disadvantage causing hypoventilation (inadequate ventilation) and hypercapnia (increased carbon dioxide).
Once pathological changes occur they are not reversible so early intervention is best, however once smoking has stopped, the disease progression can be halted and management techniques can be introduced.
EMPYSEMA
This is the abnormal permanent enlargement of gas exchange airways (pictured) accompanied by destruction of alveolar walls. Obstruction results from changes in lung tissue, rather than mucus production and inflammation. The major mechanism of airflow limitation is loss of elastic recoil.
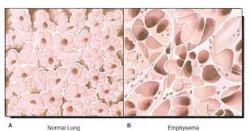
Emphysema
CAUSES
- Cigarette smoking
- Air pollution
- Childhood respiratory infections (such as diphtheria)
Inhaled oxidants in tobacco smoke and air pollution stimulate inflammation, which over time cause alveolar destruction and loss of normal elastic recoil of the bronchi. This produces large air spaces which become less effective in gas exchange. The loss of alveolar tissue means a loss of the respiratory membrane where gases cross between air and the blood, resulting in what is called ventilation-perfusion mismatching and hypoxemia (low oxygen levels in the blood). Loss of recoil also reduces the volume of air that can be expired and it is trapped in the lungs. This causes an increase in expansion of the chest and increased workload of breathing.
NUTRITION
Malnutrition is a major concern for individuals with COPD because they have increased energy expenditure, decreased energy intake and impaired oxygenation.
Please contact your doctor or visit your naturopath if you have any concerns about the health of your lungs.
Info: Craft, Gordon, Tiziani; Hechtman; Sarris and Wardle
Diabetes
DIABETES MELLITUS – IS IT CURABLE?
We know it’s an EPIDEMIC with over225,000 kiwis suffering and more than 50 people diagnosed a day.
WHAT IS IT?
It means increased sweet urine and there are three types - type I, type 2 and gestational, with glucose intolerance being the common thread.
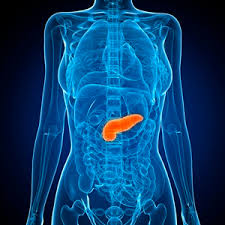
The pancreas
Insulin released (from the beta cells at the Islets of Langerhans) in the pancreas is like a key that unlocks certain cells to let the glucose pass through. If there is not enough insulin or the cells don’t let insulin unlock them, then excess glucose stays in the blood stream.
TYPE 1 - absolute insulin deficiency, because most of the beta cells have been destroyed by the body’s own autoimmune response.
Common symptoms:
- Polyphagia (excess hunger to replace lost nutrients because glucose can’t get into cells)
- Polyuria (excess urination to excrete excess blood glucose – called glycosuria)
- Polydipsia (thirst because water is also drawn into the urine leading to dehydration)
- Fatigue (through deficient energy production from low glucose absorption)
- Weight reduction (because fats are used instead of glucose for energy)
Treatment can include reducing the autoimmune response which is damaging the beta cells.
TYPE 2 – this is about cells resisting the insulin – and is the most common. With similar symptoms the cause is usually excess nutrients, obesity (which impairs insulin secretion) and inflammation.

Insulin Resistance
Treatment
80% of type 2 DM is preventable and treatment includes exercise – which increases insulin effectiveness, correct eating and herbal support of the pancreas. Recovery has been documented in the video below.
MY ADVICE - First find the trigger. As food is our medicine – a good safe diet, specific for that person, along with carefully selected herbs and positive lifestyle changes have had proven results.
- Eliminate processed foods and ‘simple carbs’
- Eliminate foods that cause inflammation such as ‘trans’ fats etc.
- Eat healthy fat
WATCH THIS - Watch the long version (1:29)
http://topdocumentaryfilms.com/simply-raw-reversing-diabetes-in-30-days/
I’m not saying that everyone should eat only raw vegan for the rest of their lives, but a carefully managed diet along with herbs has been known to turn the disease around.
For more personalised advice (as we are all different and have specific triggers) contact me for an individualised recovery plan or check out my website: www.naturalmedicineclinic.co.nz
Osteoporosis
OSTEOPOROSIS
What is Osteoporosis?
Definition: ‘Osteo’ means bone. Bone is a living tissue and relies on a constant supply of nutrients to stay healt hy. ‘Porosis’ means porous – so ‘porous bones’.
hy. ‘Porosis’ means porous – so ‘porous bones’.
While rates of osteoporosis are increasing, and it is a large cause of mortality and morbidity – it can be prevented and treated naturally.
Osteoporosis is often undetected because it is usually without pain and the first sign of it can be a broken bone. While it can affect men (through aging) it is more common in women who have passed through menopause.
WHAT HAPPENS
Under normal circumstances the Parathyroid hormone controls blood calcium levels. If calcium levels are low the thyroid gland tells bone cells, called osteoclasts, to degrade the bone – releasing the calcium. When calcium blood stores are adequate - osteoblasts then replace the calcium that was taken. However during menopause a reduction in the hormone estrogen can cause demineralization of calcium stores at a rate the body cannot keep up with – or faster than remineralization can take place – especially if calcium blood stores are low.
THINGS THAT CONTRIBUTE
- Alcohol intake is associated with increased risk by depleting nutrients and disrupt calcium and bone homeostasis
- Low body weight – associated with small bone size
- Genetics
- Medication – corticosteroids, chemotherapeutic agents, thyroxine etc. – causing secondary osteoporosis
- Smoking – interferes with nutritional uptake
- Lack of exercise – reduces bone density
- Calcium deficiency and vitamin D – both needed to grow bone
- Digestive health – which can interfere with nutrient absorption. Over 40% of post menopausal women are low in hydrochloric acid – affecting nutrient absorption
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
- Stooped posture – causing loss of height
- A hump at the base of the neck
- Spinal deformity
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
- Increase foods that optimize nutrients for bone building – green vegetables, fermented foods
- Eat a whole food diet including omega 3 essential fatty acid consumption
- Avoid foods that deplete the body of nutrients – tannin containing beverages – tea and wine, coffee, sugary foods
EASY TIPS
- Prunes have been proven to increase bone density
- Take magnesium – which decreases bone turnover
- Get plenty of fresh air exercise and sunlight (which helps in the synthesis of vitamin D)
- Herbs: celery, cayenne, chili, turmeric
- Liquid herbs: My Wild yam cream will be beneficial – for all menopausal symptoms and for osteoporosis – as it has an estrogenic effect
|
Osteoporosis is often confused with Osteoarthritis – The differences are:
|
Please contact me if you need help with any of the above treatment options or you would like a personalised plan drawn up.
Parkinson's Disease
PARKINSON'S DISEASE
Parkinson’s Society Awareness and Appeal Week is this first week in November 1-7 2015.
I have lost a family member to Parkinson's and so have seen it first hand and it wasn’t pretty. I watched my mother progress through worsening symptoms with nothing but a couple of bottles of pills – to help control the symptoms – but with a whole set of other side effects.
Since then I have had the privilege of talking to the Parkinson’s Society in Auckland and also the joy of working with Parkinson’s sufferers, and assisting them to take back some control of their disease and their own treatment – using correct nutrition, herbs and lifestyle adjustments.
WHAT IS PARKINSONS
Parkinson Disease is a progressive brain disorder involving degeneration of the neurons of the substantia nigra (mid brain) – seen in the pic. This causes a deficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain, which travel between neurons passing on messages.
While it is believed to be idiopathic, (cause unknown), age and genetics are known contributors.
However from a naturopathic viewpoint - environmental influences are also strong contenders. Toxins can cause oxidative damage to the neurons.
This pic is an example of how oxidation can damage the cells of an apple (top) and the cells of the body (body).
Normal Oxidation
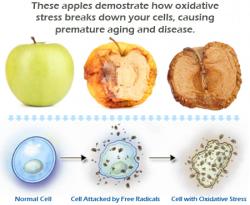
Oxidation
When food is converted to energy during normal metabolism, some oxidation occurs normally. This produces free radicals – which have an uneven number of electrons. To stabilize themselves they ‘steal’ an electron from an ‘anti’ oxidant to even up their electron numbers.
We’ve all heard of the health benefits of antioxidants. This is how they work. But if there are not enough antioxidants in the body (from a healthy diet and lifestyle) then everyday activities can create free radical damage and oxidation.
These little beastiescan also be produced during over exposure to sunlight, trauma, injury, pollution, toxins, alcohol, cigarette smoking, and processed consumables (called ‘food’).
SOME SYMPTOMS OF PARKINSON’S
- Tremor and rigidity
- Bradykinesia (slowness of movement)
- Impaired balance and coordination
- Insomnia
- Facial expression changes
- Dry or oily skin and impaired senses
PHARMACEUTICAL MEDICATION
Levodopa and carbidopa are the drugs of choice.
Levodopa passes through the blood brain barrier where it converts to dopamine, while Carbidopa stays busy supporting levodopa by preventing it from breaking down, before it reaches its target. It also helps reduce the side effects of levodopa - which include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and heart problems.
This is all well and good but unfortunately these medications are known to lose their effectiveness over time, and they don’t repair any neuron damage or get to the cause of the problem.
NATUROPATHY
From a naturopathic point of view – the cause of the condition in each individual needs a good serious look at – because it will be different in different people. It will be a mixture of genetics, lifestyle and environmental factors. As already pointed out – whatever the cause – it will result in oxidative damage. So treatment involves first finding and eliminating the cause, thereby reducing the oxidative stress, and doing some running repairs – using a broad spectrum approach involving nutrition, herbs and lifestyle changes.
Easy tip:
- Eat antioxidant rich foods every day including: most berries such as blueberries, strawberries, cranberry, blackberry, raspberry, walnuts and pecans, prunes and plums, apples, cloves, cacao and cinnamon.
|
I have seen people respond really well, improve their balance and gain vitality from: - A good exercise and stretching regime - ‘Specific ‘massage and other body treatments for that particular individual - Antioxidant rich foods including spices - Antioxidant rich herbal formulas - Cognition enhancing and neuro protective herbal formulas – to support and modulate brain cell health |
Please contact me if you need help with any of the above treatment options or you would like a personalised plan drawn up.